1.Redis基础
Redis
Redis是一种键值型的NoSql数据库
-
键值型,是指Redis中存储的数据都是以key.value对的形式存储,而value的形式多种多样,可以是字符串.数值,甚至json
-
NoSQL(Not Only SQL)数据库泛指非关系型的数据库,是为了解决大规模数据集合多重数据种类带来的挑战衍生的产物
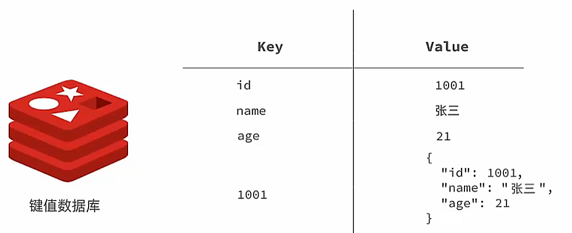
Redis是一种键值型的NoSql数据库
键值型,是指Redis中存储的数据都是以key.value对的形式存储,而value的形式多种多样,可以是字符串.数值,甚至json
NoSQL(Not Only SQL)数据库泛指非关系型的数据库,是为了解决大规模数据集合多重数据种类带来的挑战衍生的产物

Oracle 配置 :全局数据库名:orcl 管理口令:123456
scott 密码: scott
hr 密码:hr
当oracle数据库配置完成,检查Oracle服务是否正常启动
sql server t-sql高级查询
新增字段:
alter table [表名] add [字段名] nvarchar (50) null
alter table [表名]
alter column [字段名] varchar(100) not null
--删除字段:
alter table [表名] drop column [字段名]
--修改字段:
alter table [表名] alter column [字段名] nvarchar (50) null
--重命名表:(access 重命名表,请参考文章:在access数据库中重命名表)
sp_rename '表名', '新表名', 'object'
--新建约束:
alter table [表名] add constraint 约束名 check ([约束字段] <= '2000-1-1')
--删除约束:
alter table [表名] drop constraint 约束名
--新建默认值
alter table [表名] add constraint 默认值名 default '51windows.net' for [字段名]
--删除默认值
alter table [表名] drop constraint 默认值名
高级查询在数据库中用得是最频繁的,也是应用最广泛的
基本常用查询
--select
select * from student;
--all 查询所有
select all sex from student;
--distinct 过滤重复
select distinct sex from student;
--count 统计
select count(*) from student;
select count(sex) from student;
select count(distinct sex) from student;
--top 取前n条记录
select top 3 * from student;
--alias column name 列重命名
select id as 编号, name '名称', sex 性别 from student;
--alias table name 表重命名
select id, name, s.id, s.name from student s;
--column 列运算
select (age + id) col from student;
select s.name + '-' + c.name from classes c, student s where s.cid = c.id;
--where 条件
select * from student where id = 2;
select * from student where id > 7;
select * from student where id < 3;
select * from student where id <> 3;
select * from student where id >= 3;
select * from student where id <= 5;
select * from student where id !> 3;
select * from student where id !< 5;
--and 并且
select * from student where id > 2 and sex = 1;
--or 或者
select * from student where id = 2 or sex = 1;
--between ... and ... 相当于并且
select * from student where id between 2 and 5;
select * from student where id not between 2 and 5;
--like 模糊查询
select * from student where name like '%a%';
select * from student where name like '%[a][o]%'; --中间字符含a,o的
select * from student where name not like '%a%';
select * from student where name like 'ja%'; --开头含ja的
select * from student where name not like '%[j,n]%';
select * from student where name like '%[j,n,a]%'; --中间字符含j,n,a中任意一
select * from student where name like '%[^ja,as,on]%';
select * from student where name like '%[ja_on]%';
--in 子查询
select * from student where id in (1, 2);
--not in 不在其中
select * from student where id not in (1, 2);
--is null 是空
select * from student where age is null;
--is not null 不为空
select * from student where age is not null;
--order by 排序
select * from student order by name;
select * from student order by name desc;
select * from student order by name asc;
--group by 分组
按照年龄进行分组统计
select count(age), age from student group by age;
按照性别进行分组统计
select count(*), sex from student group by sex;
按照年龄和性别组合分组统计,并排序
select count(*), sex from student group by sex, age order by age;
按照性别分组,并且是id大于2的记录最后按照性别排序
select count(*), sex from student where id > 2 group by sex order by sex;
查询id大于2的数据,并完成运算后的结果进行分组和排序
select count(*), (sex * id) new from student where id > 2 group by sex * id order by sex * id;
--group by all 所有分组
按照年龄分组,是所有的年龄
select count(*), age from student group by all age;
--having 分组过滤条件
按照年龄分组,过滤年龄为空的数据,并且统计分组的条数和现实年龄信息
select count(*), age from student group by age having age is not null;
按照年龄和cid组合分组,过滤条件是cid大于1的记录
select count(*), cid, sex from student group by cid, sex having cid > 1;
按照年龄分组,过滤条件是分组后的记录条数大于等于2
select count(*), age from student group by age having count(age) >= 2;
按照cid和性别组合分组,过滤条件是cid大于1,cid的最大值大于2
select count(*), cid, sex from student group by cid, sex having cid > 1 and max(cid) > 2;
? 嵌套子查询
子查询是一个嵌套在select、insert、update或delete语句或其他子查询中的查询。
任何允许使用表达式的地方都可以使用子查询。子查询也称为内部查询或内部选择,
而包含子查询的语句也成为外部查询或外部选择。
# from (select … table)示例
将一个table的查询结果当做一个新表进行查询
select * from (
select id, name from student where sex = 1
) t where t.id > 2;
上面括号中的语句,就是子查询语句(内部查询)。在外面的是外部查询,其中外部查询可以包含以下语句:
1、 包含常规选择列表组件的常规select查询
2、 包含一个或多个表或视图名称的常规from语句
3、 可选的where子句
4、 可选的group by子句
5、 可选的having子句
# 示例
查询班级信息,统计班级学生人生
select *, (select count(*) from student where cid = classes.id) as num
from classes order by num;
# in, not in子句查询示例
查询班级id大于小于的这些班级的学生信息
select * from student where cid in (
select id from classes where id > 2 and id < 4
);
查询不是班的学生信息
select * from student where cid not in (
select id from classes where name = '2班'
)
in、not in 后面的子句返回的结果必须是一列,这一列的结果将会作为查询条件对应前面的条件。如cid对应子句的id;
# exists和not exists子句查询示例
查询存在班级id为的学生信息
select * from student where exists (
select * from classes where id = student.cid and id = 3
);
查询没有分配班级的学生信息
select * from student where not exists (
select * from classes where id = student.cid
);
exists和not exists查询需要内部查询和外部查询进行一个关联的条件,
如果没有这个条件将是查询到的所有信息。如:id等于student.id;
# some、any、all子句查询示例
查询班级的学生年龄大于班级的学生的年龄的信息
select * from student where cid = 5 and age > all (
select age from student where cid = 3
);
select * from student where cid = 5 and age > any (
select age from student where cid = 3
);
select * from student where cid = 5 and age > some (
select age from student where cid = 3
);
? 聚合查询
1、 distinct去掉重复数据
select distinct sex from student;
select count(sex), count(distinct sex) from student;
2、 compute和compute by汇总查询
对年龄大于的进行汇总
select age from student
where age > 20 order by age compute sum(age) by age;
对年龄大于的按照性别进行分组汇总年龄信息
select id, sex, age from student
where age > 20 order by sex, age compute sum(age) by sex;
按照年龄分组汇总
select age from student
where age > 20 order by age, id compute sum(age);
按照年龄分组,年龄汇总,id找最大值
select id, age from student
where age > 20 order by age compute sum(age), max(id);
compute进行汇总前面是查询的结果,后面一条结果集就是汇总的信息。
compute子句中可以添加多个汇总表达式,可以添加的信息如下:
a、 可选by关键字。它是每一列计算指定的行聚合
b、 行聚合函数名称。包括sum、avg、min、max、count等
c、 要对其执行聚合函数的列
compute by适合做先分组后汇总的业务。compute by后面的列一定要是order by中出现的列。
3、 cube汇总
cube汇总和compute效果类似,但语法较简洁,而且返回的是一个结果集。
select count(*), sex from student group by sex with cube;
select count(*), age, sum(age) from student where age is not null group by age with cube;
cube要结合group by语句完成分组汇总
4.动态查询
where panelid<>-1
and ((@itemid=-1) or (itemid=@itemid))
and ((@prodorderid=-1) or (prodorderid=@prodorderid))
and ((@lineid=-1) or (resid in(select resid from #tmpres)))
and ((@opid=-1) or (opeid=@opid))
? 排序函数
排序在很多地方需要用到,需要对查询结果进行排序并且给出序号。比如:
1、 对某张表进行排序,序号需要递增不重复的
2、 对学生的成绩进行排序,得出名次,名次可以并列,但名次的序号是连续递增的
3、 在某些排序的情况下,需要跳空序号,虽然是并列
基本语法
排序函数 over([分组语句] 排序子句[desc][asc])
排序子句 order by 列名, 列名
分组子句 partition by 分组列, 分组列
# row_number函数
根据排序子句给出递增连续序号
按照名称排序的顺序递增
select s.id, s.name, cid, c.name, row_number() over(order by c.name) as number
from student s, classes c where cid = c.id;
# rank函数函数
根据排序子句给出递增的序号,但是存在并列并且跳空
顺序递增
select id, name, rank() over(order by cid) as rank from student;
跳过相同递增
select s.id, s.name, cid, c.name, rank() over(order by c.name) as rank
from student s, classes c where cid = c.id;
# dense_rank函数
根据排序子句给出递增的序号,但是存在并列不跳空
不跳过,直接递增
select s.id, s.name, cid, c.name, dense_rank() over(order by c.name) as dense
from student s, classes c where cid = c.id;
# partition by分组子句
可以完成对分组的数据进行增加排序,partition by可以与以上三个函数联合使用。
利用partition by按照班级名称分组,学生id排序
select s.id, s.name, cid, c.name, row_number() over(partition by c.name order by s.id) as rank
from student s, classes c where cid = c.id;
select s.id, s.name, cid, c.name, rank() over(partition by c.name order by s.id) as rank
from student s, classes c where cid = c.id;
select s.id, s.name, cid, c.name, dense_rank() over(partition by c.name order by s.id) as rank
from student s, classes c where cid = c.id;
# ntile平均排序函数
将要排序的数据进行平分,然后按照等分排序。ntile中的参数代表分成多少等分。
select s.id, s.name, cid, c.name,
ntile(5) over(order by c.name) as ntile
from student s, classes c where cid = c.id;
? 集合运算
操作两组查询结果,进行交集、并集、减集运算
1、 union和union all进行并集运算
--union 并集、不重复
select id, name from student where name like 'ja%'
union
select id, name from student where id = 4;
--并集、重复
select * from student where name like 'ja%'
union all
select * from student;
2、 intersect进行交集运算
--交集(相同部分)
select * from student where name like 'ja%'
intersect
select * from student;
3、 except进行减集运算
--减集(除相同部分)
select * from student where name like 'ja%'
except
select * from student where name like 'jas%';
? 公式表表达式
查询表的时候,有时候中间表需要重复使用,这些子查询被重复查询调用,不但效率低,
而且可读性低,不利于理解。那么公式表表达式可以解决这个问题。
可以将公式表表达式(cet)视为临时结果集,
在select、insert、update、delete或是create view语句的执行范围内进行定义。
--表达式
with statnum(id, num) as
(
select cid, count(*)
from student
where id > 0
group by cid
)
select id, num from statnum order by id;
with statnum(id, num) as
(
select cid, count(*)
from student
where id > 0
group by cid
)
select max(id), avg(num) from statnum;
? 连接查询
1、 简化连接查询
--简化联接查询
select s.id, s.name, c.id, c.name from student s, classes c where s.cid = c.id;
2、 left join左连接
--左连接
select s.id, s.name, c.id, c.name from student s left join classes c on s.cid = c.id;
3、 right join右连接
--右连接
select s.id, s.name, c.id, c.name from student s right join classes c on s.cid = c.id;
4、 inner join内连接
--内连接
select s.id, s.name, c.id, c.name from student s inner join classes c on s.cid = c.id;
--inner可以省略
select s.id, s.name, c.id, c.name from student s join classes c on s.cid = c.id;
5、 cross join交叉连接
--交叉联接查询,结果是一个笛卡儿乘积
select s.id, s.name, c.id, c.name from student s cross join classes c
--where s.cid = c.id;
6、 自连接(同一张表进行连接查询)
--自连接
select distinct s.* from student s, student s1 where s.id <> s1.id and s.sex = s1.sex;
? 函数
1、 聚合函数
max最大值、min最小值、count统计、avg平均值、sum求和、var求方差
select
max(age) max_age,
min(age) min_age,
count(age) count_age,
avg(age) avg_age,
sum(age) sum_age,
var(age) var_age
from student;
2、 日期时间函数
select dateadd(day, 3, getdate());--加天
select dateadd(year, 3, getdate());--加年
select dateadd(hour, 3, getdate());--加小时
--返回跨两个指定日期的日期边界数和时间边界数
select datediff(day, '2011-06-20', getdate());
--相差秒数
select datediff(second, '2011-06-22 11:00:00', getdate());
--相差小时数
select datediff(hour, '2011-06-22 10:00:00', getdate());
select datename(month, getdate());--当前月份
select datename(minute, getdate());--当前分钟
select datename(weekday, getdate());--当前星期
select datepart(month, getdate());--当前月份
select datepart(weekday, getdate());--当前星期
select datepart(second, getdate());--当前秒数
select day(getdate());--返回当前日期天数
select day('2011-06-30');--返回当前日期天数
select month(getdate());--返回当前日期月份
select month('2011-11-10');
select year(getdate());--返回当前日期年份
select year('2010-11-10');
select getdate();--当前系统日期
select getutcdate();--utc日期
3、 数学函数
select pi();--pi函数
select rand(100), rand(50), rand(), rand();--随机数
select round(rand(), 3), round(rand(100), 5);--精确小数位
--精确位数,负数表示小数点前
select round(123.456, 2), round(254.124, -2);
select round(123.4567, 1, 2);
4、 元数据
select col_name(object_id('student'), 1);--返回列名
select col_name(object_id('student'), 2);
--该列数据类型长度
select col_length('student', col_name(object_id('student'), 2));
--该列数据类型长度
select col_length('student', col_name(object_id('student'), 1));
--返回类型名称、类型id
select type_name(type_id('varchar')), type_id('varchar');
--返回列类型长度
select columnproperty(object_id('student'), 'name', 'precision');
--返回列所在索引位置
select columnproperty(object_id('student'), 'sex', 'columnid');
5、 字符串函数
select ascii('a');--字符转换ascii值
select ascii('a');
select char(97);--ascii值转换字符
select char(65);
select nchar(65);
select nchar(45231);
select nchar(32993);--unicode转换字符
select unicode('a'), unicode('中');--返回unicode编码值
select soundex('hello'), soundex('world'), soundex('word');
select patindex('%a', 'ta'), patindex('%ac%', 'jack'), patindex('dex%', 'dexjack');--匹配字符索引
select 'a' + space(2) + 'b', 'c' + space(5) + 'd';--输出空格
select charindex('o', 'hello world');--查找索引
select charindex('o', 'hello world', 6);--查找索引
select quotename('abc[]def'), quotename('123]45');
--精确数字
select str(123.456, 2), str(123.456, 3), str(123.456, 4);
select str(123.456, 9, 2), str(123.456, 9, 3), str(123.456, 6, 1), str(123.456, 9, 6);
select difference('hello', 'helloworld');--比较字符串相同
select difference('hello', 'world');
select difference('hello', 'llo');
select difference('hello', 'hel');
select difference('hello', 'hello');
select replace('abcedef', 'e', 'e');--替换字符串
select stuff('hello world', 3, 4, 'abc');--指定位置替换字符串
select replicate('abc#', 3);--重复字符串
select substring('abc', 1, 1), substring('abc', 1, 2), substring('hello wrold', 7, 5);--截取字符串
select len('abc');--返回长度
select reverse('sqlserver');--反转字符串
select left('leftstring', 4);--取左边字符串
select left('leftstring', 7);
select right('leftstring', 6);--取右边字符串
select right('leftstring', 3);
select lower('abc'), lower('abc');--小写
select upper('abc'), upper('abc');--大写
--去掉左边空格
select ltrim(' abc'), ltrim('# abc#'), ltrim(' abc');
--去掉右边空格
select rtrim(' abc '), rtrim('# abc# '), rtrim('abc');
6、 安全函数
select current_user;
select user;
select user_id(), user_id('dbo'), user_id('public'), user_id('guest');
select user_name(), user_name(1), user_name(0), user_name(2);
select session_user;
select suser_id('sa');
select suser_sid(), suser_sid('sa'), suser_sid('sysadmin'), suser_sid('serveradmin');
select is_member('dbo'), is_member('public');
select suser_name(), suser_name(1), suser_name(2), suser_name(3);
select suser_sname(), suser_sname(0x01), suser_sname(0x02), suser_sname(0x03);
select is_srvrolemember('sysadmin'), is_srvrolemember('serveradmin');
select permissions(object_id('student'));
select system_user;
select schema_id(), schema_id('dbo'), schema_id('guest');
select schema_name(), schema_name(1), schema_name(2), schema_name(3);
7、 系统函数
select app_name();--当前会话的应用程序名称
select cast(2011 as datetime), cast('10' as money), cast('0' as varbinary);--类型转换
select convert(datetime, '2011');--类型转换
select coalesce(null, 'a'), coalesce('123', 'a');--返回其参数中第一个非空表达式
select collationproperty('traditional_spanish_cs_as_ks_ws', 'codepage');
select current_timestamp;--当前时间戳
select current_user;
select isdate(getdate()), isdate('abc'), isnumeric(1), isnumeric('a');
select datalength('abc');
select host_id();
select host_name();
select db_name();
select ident_current('student'), ident_current('classes');--返回主键id的最大值
select ident_incr('student'), ident_incr('classes');--id的增量值
select ident_seed('student'), ident_seed('classes');
select @@identity;--最后一次自增的值
select identity(int, 1, 1) as id into tab from student;--将studeng表的烈属,以/1自增形式创建一个tab
select * from tab;
select @@rowcount;--影响行数
select @@cursor_rows;--返回连接上打开的游标的当前限定行的数目
select @@error;--t-sql的错误号
select @@procid;
8、 配置函数
set datefirst 7;--设置每周的第一天,表示周日
select @@datefirst as '星期的第一天', datepart(dw, getdate()) as '今天是星期';
select @@dbts;--返回当前数据库唯一时间戳
set language 'italian';
select @@langid as 'language id';--返回语言id
select @@language as 'language name';--返回当前语言名称
select @@lock_timeout;--返回当前会话的当前锁定超时设置(毫秒)
select @@max_connections;--返回sql server 实例允许同时进行的最大用户连接数
select @@max_precision as 'max precision';--返回decimal 和numeric 数据类型所用的精度级别
select @@servername;--sql server 的本地服务器的名称
select @@servicename;--服务名
select @@spid;--当前会话进程id
select @@textsize;
select @@version;--当前数据库版本信息
9、 系统统计函数
select @@connections;--连接数
select @@pack_received;
select @@cpu_busy;
select @@pack_sent;
select @@timeticks;
select @@idle;
select @@total_errors;
select @@io_busy;
select @@total_read;--读取磁盘次数
select @@packet_errors;--发生的网络数据包错误数
select @@total_write;--sqlserver执行的磁盘写入次数
select patindex('%soft%', 'microsoft sqlserver');
select patindex('soft%', 'software sqlserver');
select patindex('%soft', 'sqlserver microsoft');
select patindex('%so_gr%', 'jsonisprogram');
10、 用户自定义函数
# 查看当前数据库所有函数
--查询所有已创建函数
select definition,* from sys.sql_modules m join sys.objects o on m.object_id = o.object_id
and type in('fn', 'if', 'tf');
# 创建函数
if (object_id('fun_add', 'fn') is not null)
drop function fun_add
go
create function fun_add(@num1 int, @num2 int)
returns int
with execute as caller
as
begin
declare @result int;
if (@num1 is null)
set @num1 = 0;
if (@num2 is null)
set @num2 = 0;
set @result = @num1 + @num2;
return @result;
end
go
调用函数
select dbo.fun_add(id, age) from student;
--自定义函数,字符串连接
if (object_id('fun_append', 'fn') is not null)
drop function fun_append
go
create function fun_append(@args nvarchar(1024), @args2 nvarchar(1024))
returns nvarchar(2048)
as
begin
return @args + @args2;
end
go
select dbo.fun_append(name, 'abc') from student;
# 修改函数
alter function fun_append(@args nvarchar(1024), @args2 nvarchar(1024))
returns nvarchar(1024)
as
begin
declare @result varchar(1024);
--coalesce返回第一个不为null的值
set @args = coalesce(@args, '');
set @args2 = coalesce(@args2, '');;
set @result = @args + @args2;
return @result;
end
go
select dbo.fun_append(name, '#abc') from student;
# 返回table类型函数
--返回table对象函数
select name, object_id, type from sys.objects where type in ('fn', 'if', 'tf') or type like '%f%';
if (exists (select * from sys.objects where type in ('fn', 'if', 'tf') and name = 'fun_find_sturecord'))
drop function fun_find_sturecord
go
create function fun_find_sturecord(@id int)
returns table
as
return (select * from student where id = @id);
go
select * from dbo.fun_find_sturecord(2);
#执行带返回值的过程。
declare @p4 int
set @p4=-1
declare @p5 varchar(255)
set @p5=''''''
exec proc '',1,'',@p4 output,@p5 output
select @p4, @p5
# 查询带%的
case when perdd_standard <> 0
then ltrim(str(perdd_actual/perdd_standard*100,10,2)) + '%'
else '0.0%' end as perdd_efff from perdd_det
# 打开远程服务器
select a.* opendatasource('SQLOLEDB','Data Source=192.168.1.XX;User ID=user;Password=pwd').DB_Name.dbo.table_name
# 查看系统有没有死锁
use master
select * from sysprocesses where blocked<>0
--找到spid
exec sp_lock
--根据spid找到objid
select object_name(85575343)
--根据objid找到表名
多表join做update
update t1 set col1=t2.col1
from table1 t1
inner join table2 t2 on t1.col2=t2.col2
sqlite中可转换为 如下语法
update table1 set col1=(select col1 from table2 where col2=table1.col2)
# with (nolock) 用法
1:使用with(nolock)时查询不受其它排他锁阻塞
begin tran
update si_mstr set si_company = '1000' where si_site = '1000'
--rollback tran
另开查询窗口,会发现查不出来
select * from si_mstr
此时要用with (nolock) ,能查,但会出现脏读,如果事务回滚会出现查询和实际数据不一致
select * from si_mstr with (nolock)
2.写法
select * from test nolock --表别名的写法
select * from test (nolock); --sql 2008以下写法
select * from test with(nolock); --完全写法
#存储过程参数赋默认值
create procedure dbo.my_proc
@first int = null, -- null default value
@second int = 2, -- default value of 2
@third int = 3 -- default value of 3
as
set nocount on;
select @first, @second, @third;
go
#分页查询
--分页1 select top 3 * from student where [sId] not in (select top (3*(4-1)) [sid] from student)--4表示页数 select *, row_number() over(order by [sage] desc ) from student-- row_number() over (order by..)获取行号
--分页2 select * from (select *, row_number() over(order by [sid] desc ) as num from student)as t where num between (Y-1)*T+1 and Y*T order by [sid] desc
--分页3 select * from (select ROW_NUMBER() over( order by [UnitPrice] asc) as num,* from [Books] where [publisherid]=1 )as t where t.num between 1 and 20 --要查询的开始条数和结束条数
[TOC]
条件:2张表的字段一致,且插入全部数据
执行:INSERT INTO 目标表 SELECT * FROM 来源表;
insert into static_data select * from industry;
[TOC]
要使用CUBE,首先要了解GROUP BY
其实CUBE和ROLLUP区别不太大,只是在基于GROUP BY 子句创建和汇总分组的可能的组合上有一定差别,CUBE将返回的更多的可能组合
CUBE和ROLLUP之间的区别在于:
CUBE生成的结果集显示了所选列中值的所有组合的聚合
ROLLUP生成的结果集显示了所选列中值的某一层次结构的聚合
[TOC]
PL/SQL(Procedure Language/SQL)
PLSQL是Oracle对sql语言的过程化扩展
指在SQL命令语言中增加了过程处理语句(如分支、循环等),使SQL语言具有过程处理能力
把SQL语言的数据操纵能力与过程语言的数据处理能力结合起来,使得PLSQL面向过程但比过程语言简单、高效、灵活和实用
Plsql(oracle), Transact-sql(SQL server)
[TOC]
视图基本概念
视图是一种虚表,只有逻辑定义,从相对概念上理解视图不占用物理空间(视图本身的定义语句还是要存储在数据字典中)
视图是建立在已有表的基础上,视图来源与建立的这些表称为基表(数据库中保存数据的实体)
[TOC]
Oracle公司成立于1977年,总部位于美国加州,是世界领先的信息管理软件开发商,因其复杂的关系数据库产品而闻名。Oracle数据库产品为财富排行榜上的前1000家公司所采用,许多大型网站也选用了Oracle系统。
Oracle数据库是Oracle(中文名称叫甲骨文)公司的核心产品,Oracle数据库是一个适合于大中型企业的数据库管理系统。在所有的数据库管理系统中(比如:微软的SQL Server,IBM的DB2等),Oracle的主要用户涉及面非常广,包括:银行、电信、移动通信、航空、保险、金融、电子商务和跨国公司等。
数据库设计:CDM&PDM设计
<1>系统管理员信息表(sys_admin)
| 字段名 | 字段值 | 数据类型 | 是否主键 | 可否为空 | 注释 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 管理员编号 | admin_num | varchar(10) | 是 | 否 | 管理员编号 |
| 管理员账号 | admin_account | varchar(10) | 否 | 否 | 管理员账号 |
| 姓名 | admin_name | varchar(10) | 否 | 否 | 姓名 |
| 密码 | admin_pwd | varchar(10) | 否 | 否 | 密码 |
| 登入时间 | login_time | datetime | 否 | 否 | 登入时间 |
| 登出时间 | loginout_time | datetime | 否 | 否 | 登出时间 |
借助Microsoft visio2003来设计无人超市管理系统的基本流程图模型
1) 熟悉visio的工作环境及组成;
2) 掌握visio软件绘制图变的基本操作;
3) 熟练使用visio的图形模版绘制出专业图表。
1) 通过打开模版并向图表添加形状来开始创建图表
2) 在图表中移动形状并调整形状的大小
3) 向表中添加文本
4) 连接图表中的形状
5) 设置图表中形状的格式
6) 保存图表以完成