JAVA多线程代码题
JAVA多线程代码题
学习核心
掌握高频问题:
- ① 双线程 轮流打印 1-100
- ② 单例模式
- ③ 生产者-消费者模式
额外扩展(关注LeetCode代码题目)
常见题型分类
① 多线程轮流打印数字、多线程分奇偶打印
- 思路1**(锁+条件变量)**:
synchronized(对象锁、wait/notifyAll) +counter(全局计数器)+mark(全局打印标识,标记目前轮到哪个线程的打印轮次) - 思路2**(基于信号量实现互斥锁)**:基于
counter(全局计数器) +Semaphore信号量实现互斥锁(一共仅有1个许可证,需要通过"传递"的方式处理保持互斥)- 每个线程有自己独立的
Semaphore对象(例如线程A向s1申请许可证,如果申请成功(s1许可证-1)则处理+1,然后传递给下一个(s2执行release操作,s2中许可证+1),依次类推,确保许可证始终只有1个可用)
- 每个线程有自己独立的
- 思路3**(借助
LockSupport完成线程的阻塞和唤醒)**:LockSupport是一个线程操作工具类(park阻塞当前线程,unpack唤醒指定线程)- 对于线程A:A先执行,唤醒B,随后阻塞A等待其他线程的唤醒
- 对于线程B:阻塞B(等待A的唤醒),执行操作,唤醒A
- 思路4(基于
AtomicInteger和自旋锁(while循环)) - 思路5(
BlockingQueue):定义两个BlockingQueue,一个队列取出任务执行后,将下一个任务加入另一个队列,交替执行 - 思路6(
ReentrantLock+Condition)
- 思路1**(锁+条件变量)**:
② 多线程交替打印字母、数字
- 核心思路:分别定义两个计数器(字母计数器、数字计数器)和打印标识(
mark用于控制哪个线程可执行操作),然后参考上述思路实现交替打印操作- 需要理解每个计数器需要打印到什么位置(监听范围、监听打印标识)
- 数字和字母转化:将数字转化为字母可以用
Character.toChars('a' + 0)标识将数字0变成a,基于此可以通过计数器形式完成字母递增,只需要在打印的时候转化一下即可(还有一种方式是定义数组存储字母集,然后通过下标数字索引来与字母对照) - 常见题型:
a1b2c3d4....z26(字母数字交替打印)a1b2c3d4a1b2c3d4.....(abcd、1234交替打印,打印10个轮次)AbCdEf....(字母大小写交替打印)
- 核心思路:分别定义两个计数器(字母计数器、数字计数器)和打印标识(
③ **如何控制多线程场景下任务的顺序执行?**例如要实现
t1->t2->t3的线程任务的执行顺序- 思路1:纯
join方式,每个线程严格遵循start、join的执行组合,当前面的任务执行完成才开启下一个组合 - 思路2:
join+CountDownLatchjoin:此处join用于确保所有子线程都执行完成,用于阻塞主线程(只有当所有任务执行完成,主线程才继续往下)CountDownLatch:CountDownLatch用于同步控制,定义两个计数器(初始化为1)分别用于控制t1->t2、t2->t3的同步- 当
cdl减少为0才能执行,否则会阻塞当前线程,因此其同步控制分析如下- 当任务
t1执行完成,cdl_1减1(执行countDown) - 在任务
t2执行前调用cdl_1.await()方法(只有当计数器减为0才继续执行),即当上述任务t1完成后t2就可以执行了。当t2执行完成,cdl_2减1 - 同理,在任务
t3执行前调用cdl_2.await()方法,即只有t2执行完成后cdl_2计数器减为0后t3才可以继续执行
- 当任务
- 当
- 思路1:纯
④ 模拟窗口卖票(开设4个窗口进行售票,如何确保正常售票?)
- 分析:每个线程是1个购票窗口,模拟购票操作
- 思路1:
synchronized:对共享资源进行加锁- 特点:简单易用,适用于简单的线程同步场景
- 思路2:
AtomicInteger:用AtomicInteger保证余票的线程安全- 特点:无锁实现,性能较高
- 思路3:
ReentrantLock可重入锁(lock、unlock)- 特点:更为灵活,支持公平锁和非公平锁
- 思路4:
Semaphore信号量- 特点:适合控制并发访问的场景
学习资料
1.写一个双线程轮流打印1-100
❌ AtomicInteger :在其他加锁的方案中counter(全局计数器)是否一定要定义为AtomicInteger类型。此处的误区在于没有理解线程控制的解决方案(概念混淆),实际上【AtomicInteger+自旋锁】(无锁方案)本身也是用于解决这个场景问题的一种方案,在其他一些加锁方案中,盲目使用反而有种脱裤子放屁的感觉,因为本身的场景就是对counter这个共享资源的控制,如果用了其他的加锁方案,实际上counter本身用普通变量定义即可。而【AtomitInteger+自旋锁】则是基于另一种方案的思路
① 锁 + 条件变量
思路1:对象锁lock:wait/notifyAll + 等待标记mark
- 核心
- 参数:全局计数器(counter(可定义为普通变量))、对象锁(lock)、全局等待标记(mark)
思路分析:构建2个线程,其主要的工作是监听当前counter是否达到100,如果没有则需要打印数据(而打印的这块代码则是需要进行加锁synchronized),加锁的部分主要进一步校验是否到自己的打印轮次,如果没有轮到(根据全局等待标记)则继续等待,如果轮到则执行打印操作、唤醒其他所有线程并切换标记,将代码的执行权交出去
class ThreadDemo1_01 {
static AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger(1); // 定义计数器
static Object lock = new Object(); // 定义对象锁
static int mark = 1; // 定义全局等待标记(1-线程A执行;2-线程B执行)
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 线程A定义
Thread ta = new Thread(() -> {
while (count.get() < 100) {
synchronized (lock) {
while (mark != 1) {
try {
lock.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
System.out.println("线程A执行" + count.getAndIncrement()); // 打印并执行自增操作
lock.notifyAll(); // 唤醒
mark = 2; // 切换等待标记
}
}
});
// 线程B定义
Thread tb = new Thread(() -> {
while (count.get() <= 100) {
synchronized (lock) {
while (mark != 2) {
try {
lock.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
System.out.println("线程B执行" + count.getAndIncrement()); // 线程B打印信息
lock.notifyAll(); // 唤醒
mark = 1; // 切换等待标记
}
}
});
// 启动线程
ta.start();
tb.start();
}
}
基于【锁+控制变量】的处理思路,可以有下述两种写法(执行效果都一样)
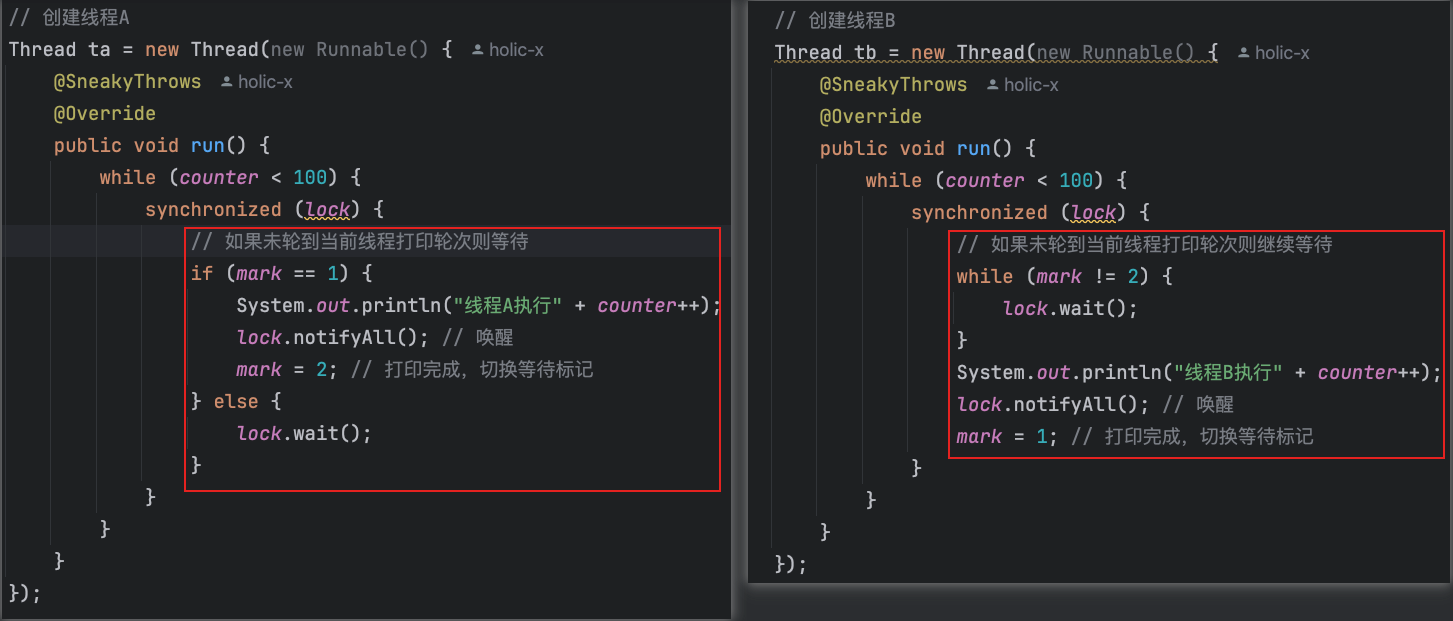
② 基于信号量Semaphore实现互斥锁
思路2:信号量Semaphore(acquire获取锁、release释放锁)
Semaphore(信号量)是一个线程同步工具,主要用于在一个时刻允许多个线程对共享资源进行并行操作的场景。通常情况下,使用Semaphore的过程实际上是多个线程获取访问共享资源许可证的过程
基于信号量实现互斥锁(设定了许可证只有1张,要么在s1那、要么在s2那,达到互斥目的,只有拿到许可证的线程才能继续往下执行,执行完成释放许可证),Semaphore 的内部逻辑分析如下
基于上述分析,线程A、B的执行逻辑分析如下:
- ① 定义核心参数:counter(全局计数器)、s1(信号量1)、s2(信号量2)
- ② 初始化许可证:s1(1张许可证)、s2(0张许可证),可以理解为只有1个共享资源(即counter),所以此处s1、s2要实现互斥锁的效果,要么许可证在s1处、要么许可证在s2处
- ③ 线程执行业务逻辑:线程要执行业务逻辑则需要申请许可证,此处将s1分配给线程A、s2分配给线程B
- 线程A 向 s1 申请许可证,初始化状态下s1有1张许可证,因此线程A申请成功,s1许可证-1,执行业务逻辑,s2执行release操作释放锁(许可证+1,可以理解为将许可证交给s2)
- 随后线程B在向s2申请许可证的时候,如果申请成功,s2许可证-1,执行业务逻辑,s1执行release操作释放锁(许可证+1,可以理解为随后将许可证交给s1)
class ThreadDemo1_02 {
// 思路:信号量思路(基于信号量实现互斥锁)
static AtomicInteger counter = new AtomicInteger(1); // 计数器
static Semaphore s1 = new Semaphore(1); // 初始化许可证为1
static Semaphore s2 = new Semaphore(0); // 初始化许可证为0
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 线程A定义
Thread threadA = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@SneakyThrows
@Override
public void run() {
while (counter.get() < 100) {
s1.acquire(); // s1获取锁(许可证-1)
System.out.println("线程A:" + counter.getAndIncrement());
s2.release(); // s2释放锁(许可证+1)
}
}
});
// 线程B定义
Thread threadB = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@SneakyThrows
@Override
public void run() {
while (counter.get() < 100) {
s2.acquire(); // s2获取锁(许可证-1)
System.out.println("线程B:" + counter.getAndIncrement());
s1.release(); // s1释放锁(许可证+1)
}
}
});
// 启动线程进行测试
threadA.start();
threadB.start();
}
}
③ 基于LockSupport的阻塞和唤醒方法
思路3:LockSupport
LockSupport定义了一组的公共静态方法,这些方法提供了最基本的线程阻塞和唤醒功能,而LockSupport也成为构建同步组件的基础工具
class ThreadDemo1_03 {
static AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger(1); // 定义计数器
static Thread[] threads = new Thread[2];
public static void main(String[] args) {
threads[0] = new Thread(()->{
while(count.get() < 100) {
System.out.println("线程A执行" + count.getAndIncrement());
LockSupport.unpark(threads[1]);
LockSupport.park();
}
});
threads[1] = new Thread(()->{
while(count.get() < 100) {
LockSupport.park();
System.out.println("线程B执行" + count.getAndIncrement());
LockSupport.unpark(threads[0]);
}
});
threads[0].start();
threads[1].start();
}
}
另一种版本写法
import java.util.concurrent.locks.LockSupport;
public class LockSupportExample {
private static Thread t1, t2;
public static void main(String[] args) {
t1 = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i += 2) {
System.out.println("Thread 1: " + i);
LockSupport.unpark(t2); // 唤醒线程2
LockSupport.park(); // 阻塞当前线程
}
});
t2 = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 2; i <= 100; i += 2) {
LockSupport.park(); // 阻塞当前线程,等待线程1的唤醒
System.out.println("Thread 2: " + i);
LockSupport.unpark(t1); // 唤醒线程1
}
});
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
④ 基于AtomicInteger和自旋锁(while循环条件)
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
public class AtomicIntegerExample {
private static final AtomicInteger number = new AtomicInteger(1);
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(() -> {
while (number.get() <= 100) {
if (number.get() % 2 == 1) {
System.out.println("Thread 1: " + number.getAndIncrement());
}
}
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
while (number.get() <= 100) {
if (number.get() % 2 == 0) {
System.out.println("Thread 2: " + number.getAndIncrement());
}
}
}).start();
}
}
同题目:【2个线程,交替打印1-100的奇偶数】
其本质上是一样的概念,但此处需做额外的奇数、偶数判断(此处以思路2进行参考),对比思路2代码,其在内存嵌套中多加了个while判断,用于明确限定奇数、偶数的打印
class ThreadDemo1_04 {
static AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger(1); // 定义计数器
static Semaphore s1 = new Semaphore(1);
static Semaphore s2 = new Semaphore(0);
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 线程A打印奇数
Thread ta = new Thread(() -> {
while (count.get() < 100) {
while (count.get() % 2 == 1) {
try {
s1.acquire();
System.out.println("[奇数]线程A执行" + count.getAndIncrement());
s2.release();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
});
// 线程B打印偶数
Thread tb = new Thread(() -> {
while (count.get() <= 100) {
while (count.get() % 2 == 0) {
try {
s2.acquire();
System.out.println("[偶数]线程B执行" + count.getAndIncrement());
s1.release();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
});
ta.start();
tb.start();
}
}
⑤ BlockingQueue阻塞队列
- 使用两个
BlockingQueue作为线程间的通信工具 - 一个线程将任务放入队列,另一个线程从队列中取出任务并执行
- 通过队列的阻塞特性实现线程的交替执行
public class Solution001_05 {
private static AtomicInteger counter = new AtomicInteger(1);
private static final BlockingQueue<Integer> queue1 = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>();
private static final BlockingQueue<Integer> queue2 = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>();
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread ta = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@SneakyThrows
@Override
public void run() {
while (counter.get() < 100) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + queue1.take());
queue2.offer(counter.getAndIncrement());
}
}
}, "线程A");
Thread tb = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@SneakyThrows
@Override
public void run() {
while (counter.get() < 100) {
queue1.offer(counter.getAndIncrement());
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + queue2.take());
}
}
}, "线程B");
ta.start();
tb.start();
}
}
⑥ ReentrantLock + Condition
public class Solution001_06 {
static int counter = 1;
static ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
static Condition condition = lock.newCondition();
static int mark = 1;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread ta = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@SneakyThrows
@Override
public void run() {
while (counter < 100) {
// 加锁
lock.lock();
while (mark != 1) {
condition.await(); // 等待唤醒
}
// 实现逻辑
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + (counter++));
condition.signal(); // 唤醒其他线程
mark = 2; // 切换打印标识
// 解锁
lock.unlock();
}
}
}, "线程A");
Thread tb = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@SneakyThrows
@Override
public void run() {
while (counter < 100) {
// 加锁
lock.lock();
while (mark != 2) {
condition.await(); // 等待唤醒
}
// 实现逻辑
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + (counter++));
condition.signal(); // 唤醒其他线程
mark = 1; // 切换打印标识
// 解锁
lock.unlock();
}
}
}, "线程B");
ta.start();
tb.start();
}
}
2.三个线程顺序打出1-100
和前面的双线程打印思路类似,需要引入一个计数器、锁(Lock)或者信号量、mark(打印标记,用于控制哪个线程打印什么范围的内容)
类似的,参考【题目1】中的思路1,三个线程轮流打印就是通过控制mark标记进而控制顺序打印(如果当前不是自己的轮次则等待,是则执行),打印后确认打印的范围(如果超出范围,例如多打印了101则通过if语句过滤掉,跳出当次循环)
/**
* 三线程轮流打印1-100
* 解决思路1:对象锁+全局标识
*/
public class Solution1 {
// 锁思路:对象锁+全局标识
static Object lock = new Object();
static AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger(1);
static int mark = 1; // 定义等待标记(为1线程A打印,为2线程B打印;为3线程C打印)
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
// 打印数字
while (count.get() < 100) {
synchronized (lock) {
while(mark !=1) {
try {
lock.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
// 排除101数字的打印
if(count.get() != 101) {
System.out.println("线程1执行" + count.getAndIncrement()); // 打印并执行自增操作
}else{
break; // 跳出当次循环
}
lock.notifyAll(); // 唤醒线程
mark = 2; // 切换等待标记
}
}
}
});
Thread t2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
// 打印数字
while (count.get() < 100) {
synchronized (lock) {
while(mark !=2) {
try {
lock.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
// 排除101数字的打印
if(count.get() != 101) {
System.out.println("线程2执行" + count.getAndIncrement()); // 打印并执行自增操作
}else{
break; // 跳出当次循环
}
lock.notifyAll(); // 唤醒线程
mark = 3; // 切换等待标记
}
}
}
});
Thread t3 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
// 打印数字
while (count.get() < 100) {
synchronized (lock) {
while(mark !=3) {
try {
lock.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
// 排除101数字的打印
if(count.get() != 101) {
System.out.println("线程3执行" + count.getAndIncrement()); // 打印并执行自增操作
}else{
break; // 跳出当次循环
}
lock.notifyAll(); // 唤醒线程
mark = 1; // 切换等待标记
}
}
}
});
// 启动线程
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
}
}
信号量方案:参考【问题1】中的信号量方案思路,此处引入3个信号量进行处理,只有获取到许可的线程才能执行(可以理解为此处的new Semphore(1)相当于一把锁,满足条件则获取许可执行,随后释放下一个信号量的许可让其他线程执行,以此类推)
/**
* 三线程轮流打印1-100
* 解决思路2:信号量方案
*/
public class Solution2 {
static AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger(1); // 定义计数器
// 信号量(分别定义三个信号量)
static Semaphore firstToSecond = new Semaphore(1);// 初始化1个许可
static Semaphore secondToThird = new Semaphore(0);
static Semaphore ThirdToFirst = new Semaphore(0);
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
// 打印数字
while (count.get() < 100) {
try {
// 获取许可
firstToSecond.acquire();
System.out.println("线程t1执行" + count.getAndIncrement());
// 释放许可
secondToThird.release();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
});
Thread t2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
// 打印数字
while (count.get() < 100) {
try {
// 值为1,获取许可,开始执行(如果值为0则进入阻塞状态)
secondToThird.acquire();
System.out.println("线程t2执行" + count.getAndIncrement());
// 释放许可
ThirdToFirst.release();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
});
Thread t3 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
// 打印数字
while (count.get() < 100) {
try {
// 值为1,获取许可,开始执行(如果值为0则进入阻塞状态)
ThirdToFirst.acquire();
System.out.println("线程t3执行" + count.getAndIncrement());
// 释放许可
firstToSecond.release();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
});
// 启动线程
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
}
}
3.多线程问题:线程A,B、C,分别打印1、2、3,顺序执行10次
类似的,也是参考上述思路。此处为了通用性处理,通过设定一个方法,可以指定线程打印指定轮次的数字。例如以count%线程数得到的余数作为轮次,线程A打印每个轮次中余数为0的数、线程B打印每个轮次中余数为1的数、线程C打印每个轮次中余数为2的数等
线程A、B、C顺序执行10次,实际上就是线程A、B、C打印从1-30的数字,只不过每个线程输出的时候输出的是x%3+1。需注意当线程卡住的时候需要思考打印标识的切换是否正常,如果切换异常就会导致整个线程卡住
例如线程A打印1、线程B打印2、线程C打印3,那么打印标识也应该在这几个数字出现轮转,如果出现不合预期的数字,则会导致打印切换失败,例如mark被切换成0,那么线程A、B、C在mark为0的时候都不满足条件,就会处于lock.wait()持续等待
/**
* 多线程问题:线程A,B、C,分别打印1、2、3,顺序执行10次
* 思路1:Lock对象锁,打印指定轮次
*/
public class Solution1 {
static Object lock = new Object(); // 定义对象锁
static AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger(1);// 定义计数器
public static void printNum(int turn){
// 判断是否为当前轮次
while(count.get()<10){ // 此处用同一个计数器,那么数字应该要打印到30(即counter<30)
synchronized (lock){
// 判断是否为当前轮次,如果不是则等待
while(count.get()%3!=turn){
try {
lock.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
// 是当前轮次,则打印数字并执行自增
System.out.println( Thread.currentThread().getName() + "线程执行:" + count.getAndIncrement());
// 唤醒其他线程
lock.notifyAll();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义线程A 打印轮次0
Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
printNum(0);
}
},"A");
// 定义线程B 打印轮次1
Thread t2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
printNum(1);
}
},"B");
// 定义线程C 打印轮次2
Thread t3 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
printNum(2);
}
},"C");
// 线程启动
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
}
}
4.计数累加怎么线程安全,可以怎么实现,100个线程,每个线程累加100次
核心:多线程计数安全累加,通过线程池+AtomicInteger进行操作
提交100个任务,每个任务执行100次累加操作,通过线程池定义100个线程执行这些批次任务
/**
* 计数安全累加问题:100个线程,每个线程累加100次
* 思路:线程池 + AtomicInteger
*/
public class Solution1 {
// 定义计数器(此处final修饰AtomicInteger对象表示对象不可变,其内部的值还是可变的)
private static final AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger(0);
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义线程池(固定大小100个线程)
ExecutorService executors = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(100);
// 提交100个任务,每个任务执行100次累加
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
executors.execute(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
for (int j = 0; j < 100; j++) {
// 原子操作,线程安全
count.incrementAndGet();
}
}
});
}
// 关闭线程池,不再接收新的任务
executors.shutdown();
// 输出最终统计的结果
System.out.println(count);
}
}
5.线程交叉打印12A34B56C,多种实现方式(一个打印数字,一个打印字母)
核心:回归到双线程打印思路,一个线程打印数字、一个线程打印字母,通过标识进行线程切换,如果没有到自己执行的轮次则等待,执行完成则切换mark并唤醒其他线程
/**
* 线程交叉打印12A34B56C,多种实现方式(一个打印数字,一个打印字母)
*/
public class Solution1 {
// 定义对象锁
static Object lock = new Object();
// 定义打印标识(线程1打印数字、线程2打印字母)
static int printMark = 1; // 1打印数字、2打印字母
static AtomicInteger numCount = new AtomicInteger(1); // 定义数字计数器
static AtomicInteger letterCount = new AtomicInteger(0);// 定义字母计数器
static char[] letters ={'A','B','C','D','E','F','G','H','I','J','K','L','M','N','O','P','Q','R','S','T','U','V','W','X','Y','Z'};
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义线程1 打印数字(52个数字)
Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
while(numCount.get()<=52){
synchronized(lock){
while (printMark!=1){
// 非当前轮次则等待(并非打印数字)
try {
lock.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
// 轮到打印数字,执行操作,切换标志。唤醒其他线程
System.out.println(numCount.getAndIncrement());
System.out.println(numCount.getAndIncrement());
printMark = 2;
lock.notifyAll();
}
}
}
});
Thread t2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
while(letterCount.get()<26){
synchronized(lock){
while (printMark!=2){
// 非当前轮次则等待(并非打印字母)
try {
lock.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
// 轮到打印字母,执行操作,切换标志。唤醒其他线程
System.out.println(letters[letterCount.getAndIncrement()]);
printMark = 1;
lock.notifyAll();
}
}
}
});
// 启动线程
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
6.两个线程交替打印ABCD..Z字母,一个大写一个小写
核心:回归双线程打印思路,可以定义一个数组(敲定打印序列),依次顺序打印;也可从A->Z递增,然后根据大小写打印标志进行切换转化
/**
* 两个线程交替打印ABCD..Z字母,一个大写一个小写
* 思路:回归双线程打印思路
*/
public class Solution1 {
// 定义对象锁
static Object lock = new Object();
// 定义打印标识
static int printMark = 1; // 1打印大写、2打印小写
static AtomicInteger letterCount = new AtomicInteger(0);// 定义字母计数器
static char[] letters ={'A','B','C','D','E','F','G','H','I','J','K','L','M','N','O','P','Q','R','S','T','U','V','W','X','Y','Z'};
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义线程打印大写字母
Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
while (letterCount.get()<25) {
synchronized (lock) {
// 判断是否为当前轮次(打印大写字母)
while(printMark != 1){
try {
lock.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
// 打印大写字母,计数+1,切换标志,唤醒线程
System.out.println(letters[letterCount.getAndIncrement()]);
printMark = 2;
lock.notifyAll();
}
}
}
});
// 定义线程打印小写字母
Thread t2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
while (letterCount.get()<26) {
synchronized (lock) {
// 判断是否为当前轮次
while(printMark != 2){
try {
lock.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
// 打印小写字母,计数+1,切换标志,唤醒线程
System.out.println(Character.toLowerCase(letters[letterCount.getAndIncrement()]));
printMark = 1;
lock.notifyAll();
}
}
}
});
// 启动线程
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
7.两个线程交替打印出a1b2c3.....z26
核心:双线程交替打印思路,线程1打印字母,线程2打印数字,分别定义不同的计数器打印相应的序列
(此处可以不需要指定字母序列,定义计数器通过字符操作计算即可(类似'A'+1 得到对应的字符值并转化))
/**
* 两个线程交替打印出a1b2c3.....z26
*/
public class Solution1 {
// 定义对象锁
static Object lock = new Object();
// 定义打印标识
static int printMark = 1;
// 定义数字计数器
static AtomicInteger numCount = new AtomicInteger(1);
// 定义字母计数器
static AtomicInteger letterCount = new AtomicInteger(0);
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义线程1打印数字
Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
while (numCount.get() <= 26) {
synchronized (lock) {
// 判断是否为当前轮次(打印数字)
while (printMark != 1) {
// 非打印数字轮次,持续等待
try {
lock.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
// 打印数字、计数+1、切换标识、唤醒线程
System.out.println(numCount.getAndIncrement());
printMark = 2;
lock.notifyAll();
}
}
}
});
// 定义线程2打印字母
Thread t2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
while (letterCount.get() < 26) {
synchronized (lock) {
// 判断是否为当前轮次(打印字母)
while (printMark != 2) {
// 非打印字母轮次,持续等待
try {
lock.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
// 打印字母、计数+1、切换标识、唤醒线程
System.out.println(Character.toChars('A' + letterCount.getAndIncrement()));
printMark = 1;
lock.notifyAll();
}
}
}
});
// 启动线程
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
8.两个线程,一个打印abcd,一个打印1234,需求交替打印出a1b2c3d4a1b2c3d4; 打印10轮
核心:回归双线程打印思路,一个线程打印字母,一个线程打印数字,打印的内容是在指定的集合中(可以定义数组存储,也可通过计数计算得到),对应计数器对序列长度求余得到当前要打印的位置
此处需注意打印10个轮次,即10个abcd、10个1234,那么总计数应该是40
/**
* 双线程打印:一个打印abcd,一个打印1234,交替打印a1b2c3d4a1b2c3d4; 打印10轮
*/
public class Solution2 {
// 定义对象锁
static Object lock = new Object();
// 定义打印标识(1打印字母;2打印数字)
static int printMark = 1;
// 定义字母打印计数
static AtomicInteger letterCount = new AtomicInteger(0);
// 定义数字打印计数
static AtomicInteger numCount = new AtomicInteger(1);
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义线程1打印字母
Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
while(letterCount.get() < 40) {
synchronized (lock) {
while(printMark!=1){
try {
lock.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
// 执行打印、打印自增、切换标识、唤醒线程
System.out.println(Character.toChars('a' + letterCount.getAndIncrement()%4));
printMark=2;
lock.notifyAll();
}
}
}
});
Thread t2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
while(numCount.get() < 40) {
synchronized (lock) {
while(printMark!=2){
try {
lock.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
// 执行打印、计数自增(处理临界值)、切换标识、唤醒线程
// if(numCount.getAndIncrement()%4==0){
// System.out.println(4);
// }else{
System.out.println(numCount.getAndIncrement()%4);
// }
printMark=1;
lock.notifyAll();
}
}
}
});
// 启动线程
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
9.假设有T1、T2、T3三个线程,怎样保证T2在T1执行完后执行,T3在T2执行完后执行?
① join方式
join():"加入",让主线程等待(WAITING状态),一直到调用join()方法的线程执行结束为止
// join的等效写法
thread1.join();
thread2.join();
// 等价于
while(thread1.isAlive()||thread2.isAlive()){
// 只要thread1、thread2中有一个线程还活跃,主线程就不会向下执行
}
// join的第二种等价写法
synchronized(thread1)){
thread1.wait();
}
思路1:只使用
join方法,模拟一个Task任务线程,对于每一个线程启动执行并确保执行完成后再启动下一个线程启动
t1,调用t1.join()等待t1执行完成,随后再启动t2,调用t2.join()等待t2执行完成......以此类推/** * 问题:确保t1、t2、t3线程顺序执行(t1执行完后执行t2,然后执行t3) * 思路1:只使用join方法:让主线程处于等待WAITING状态,只有调用join的线程不再活跃(执行完成)主线程才会继续往下 */ public class Solution1 { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { // 创建3个任务(线程) Thread t1 = new Thread(new Task("A")); Thread t2 = new Thread(new Task("B")); Thread t3 = new Thread(new Task("C")); // 启动线程t1,调用join方法等待线程t1执行完成 t1.start(); t1.join(); // 继续启动线程t2、调用join方法等待线程t2执行完成 t2.start(); t2.join(); // 继续启动线程t3、调用join方法等待线程t3执行完成 t3.start(); t3.join(); // 所有线程执行完成,主线程继续往下 System.out.println("所有任务执行完成"); } } /** * 定义Task任务线程 */ class Task implements Runnable { private String taskName; public Task(String taskName) { this.taskName = taskName; } @Override public void run() { // 模拟任务执行沉睡1s try { System.out.println("任务" + taskName + "执行...."); Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } }
②
join搭配CountDownLatch思路2:使用
join配合CountDownLatch的简单示例
CountDownLatch是一个同步工具类,允许一个或多个线程一直等待,直到其他线程操作执行完成之后才继续往下执行。其应用场景主要是在一些场合中需要等待某个条件达到要求才能执行后面的操作,或者是线程都完成后触发时间,以便进行后续的操作 定义两个
CountDownLatch实例分别用于控制t1->t2(t1Tot2Latch)、t2->t3(t2Tot3Latch)的执行顺序,初始计数都为1,t2的开始执行需要等待t1Tot2Latch计数减为0,t3的开始执行需要等待t2Tot3Latch计数减为0,以此确保t2在t1完成之后执行,t3在t2完成之后执行 此处
CountDownLatch的引入用于确保t1、t2、t3 的执行顺序,而join方法的引入则是用于确保所有的子线程(任务)执行完成才继续往下(即所有任务完成,主线程才继续往下) 此处
join+CountDownLatch的组合中,CountDownLatch用于控制任务的执行顺序,join则用于确保子任务均执行完成(否则继续执行主线程),对比纯粹join的方式(限定一个任务得先start启动、join在该任务执行完成之前阻塞主进程)/** * 问题:确保t1、t2、t3线程顺序执行(t1执行完后执行t2,然后执行t3) * 思路2:join + CountDownLatch 配合使用 * 定义两个CountDownLatch计数器(await\countDown方法),当t1Tot2Latch、t2Tot3Latch分别用于确保t1->t2、t2->t3的执行顺序 * t1线程:执行t1任务,执行完成后计数器t1Tot2Latch减1(表示t1执行完成,可以继续下一步) * t2线程:校验t1是否执行完成(调用t1Tot2Latch.await(),如果还没执行完成则继续等待),执行t2并计数器t2Tot3Latch减1(表示t2执行完成,可以继续下一步) * t3线程:类似地,校验t2是否执行完成,执行t3 * 最后通过join方法确保所有任务都执行完成,然后主线程才可以继续往下 * 此处t1->t2->t3的内部同步执行顺序是由CountDownLatch保证的,而所有线程执行完成才执行主线程则是通过join方法进行控制 */ public class Solution2 { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { // 定义两个计数器 CountDownLatch t1Tot2Latch = new CountDownLatch(1);// t1 -> t2 的同步(t1执行完成,计数器减1,才触发t2线程执行) CountDownLatch t2Tot3Latch = new CountDownLatch(1);// t2 -> t3 的同步(t2执行完成,计数器减1,才触发t3线程执行) // 创建3个任务(线程) Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() { @SneakyThrows @Override public void run() { System.out.println("任务" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "执行"); Thread.sleep(1000); // 模拟执行 // t1执行完成,计数器减1 t1Tot2Latch.countDown(); } }, "A"); Thread t2 = new Thread(new Runnable() { @SneakyThrows @Override public void run() { // 等待计数器减为0才执行(此处即等待t1执行完成后计数器减1成功后才执行) t1Tot2Latch.await(); System.out.println("任务" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "执行"); Thread.sleep(1000); // 模拟执行 // t2执行完成,对应计数器减1 t2Tot3Latch.countDown(); } }, "B"); Thread t3 = new Thread(new Runnable() { @SneakyThrows @Override public void run() { try { // 等待计数器减为0才执行(此处即等待t2执行完成后计数器减1成功后才执行) t2Tot3Latch.await(); System.out.println("任务" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "执行"); Thread.sleep(1000); // 模拟执行 } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } }, "C"); // 启动线程t1\t2\t3 t1.start(); t2.start(); t3.start(); // 等待所有线程执行完毕(此处t1\t2\t3的执行顺序由同步器进行控制,此处join的引入是为了确保t1\t2\t3都执行完成才继续主线程往下) t1.join(); t2.join(); t3.join(); // 可以实验下,如果此处将join注释,则可能出现主线程内容输出了但是子线程还没执行完成,因此此处要将主线程阻塞,确保所有的任务执行完成才接着往下 // 所有线程执行完成,主线程继续往下 System.out.println("所有任务执行完成"); } }
10.目前有500张票,同时有4(1~4)个购票窗口,模拟购票流程,打印购票结果,比如:从1窗口购买1张票,剩余499张票
① synchronized
定义TicketWindow模拟窗口购票行为,对外提供购票方法,使用synchronized块来同步对剩余票数的访问(避免多个线程同时修改票数导致数据不一致问题),当剩余票数为0时窗口线程停止执行
/**
* 模拟4个窗口进行售票
* 1.定义售票窗口模拟售票(一个窗口对应一个任务、线程,执行售票操作)
* 2.使用synchronized同步售票操作的票数减少,避免多线程操作导致数据不一致
* 3.售票是判断余票是否足够,如果不足则停止售票关闭窗口(线程执行结束)
*/
public class Solution010_02 {
// 定义对象锁
static Object lock = new Object();
// 剩余总票数
static int remainTicket = 20;
/**
* 模拟购票窗口
*/
static class TicketWindow implements Runnable {
private String windowName;
public TicketWindow(String windowName) {
this.windowName = windowName;
}
@SneakyThrows
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
// 同步块:操作卖票操作
synchronized (lock) {
if (remainTicket > 0) {
buyTicket();
} else {
System.out.println("票已售完,窗口" + this.windowName + "关闭");
break; // 票已售完,线程结束
}
}
// 模拟购票后的随机操作
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}
/**
* 购票
*/
private void buyTicket() {
System.out.println("窗口" + windowName + "售出一张票,当前余票" + remainTicket);
remainTicket--;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 开启4个窗口模拟售票
for (int i = 1; i <= 4; i++) {
new Thread(new TicketWindow("ticketWindow" + i)).start();
}
}
}
另一种写法
// 思路1:synchronized
public class Solution010_03 {
static Object lock = new Object(); // 对象锁
static int remindTickets = 20; // 余票定义
// 窗口定义
static class TicketWindow implements Runnable {
@SneakyThrows
@Override
public void run() {
// 模拟售票操作
while (true) {
// 对购票操作进行加锁
synchronized (lock) { // synchronized (TicketWindow.class) {
Thread.sleep(1000); // 模拟购票操作
if (remindTickets <= 0) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "已售空...");
break; // 票已售空,窗口停止售票(终止while)
} else {
remindTickets--; // 票数-1
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "售出1张票,现余票为" + remindTickets);
}
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建4个窗口
for (int i = 1; i <= 4; i++) {
new Thread(new TicketWindow(), "窗口" + i).start();
}
}
}
② AtomicInteger
4个线程 +
AtomicInteger
// 思路2:AtomicInteger
public class Solution010_04 {
static AtomicInteger remindTickets = new AtomicInteger(20); // 余票定义
// 窗口定义
static class TicketWindow implements Runnable {
@SneakyThrows
@Override
public void run() {
// 模拟售票操作
while (true) {
Thread.sleep(1000); // 模拟购票操作
if (remindTickets.get() <= 0) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "已售空...");
break; // 票已售空,窗口停止售票(终止while)
} else {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "售出1张票,现余票为" + remindTickets.getAndDecrement());
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建4个窗口
for (int i = 1; i <= 4; i++) {
new Thread(new TicketWindow(), "窗口" + i).start();
}
}
}
线程池 +
AtomicInteger
/**
* 10.有500张余票,同时有4个购票窗口,模拟购票流程,打印购票结果
* - 例如 从窗口1买入1张票,剩余499张票
*/
public class Solution010_01 {
static AtomicInteger remindTickets = new AtomicInteger(500); // 剩余500张余票
@SneakyThrows
// 定义购票方法
public static void buyTicket() {
// Thread.sleep(1000); // 模拟购票操作
// 校验当前余票
if (remindTickets.get() < 0) {
System.out.println("当前余票不足....");
} else {
// 执行购票操作
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "窗口售出1张票,剩余票数为:" + remindTickets.getAndDecrement());
}
}
@SneakyThrows
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 模拟4个购票窗口(此处用线程池处理)
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(4);
// 模拟600个抢票操作
for (int i = 0; i < 600; i++) {
executor.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
new Solution010_01().buyTicket();
}
});
}
// 关闭线程池
executor.shutdown();
// 等待线程执行完成
executor.awaitTermination(1, TimeUnit.HOURS);
System.out.println("售票结束......");
}
}
③ Semaphore 信号量
// 思路3:Semaphore
public class Solution010_05 {
static int remindTickets = 20; // 余票定义
static Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(1); // 信号量定义
// 窗口定义
static class TicketWindow implements Runnable {
@SneakyThrows
@Override
public void run() {
// 模拟售票操作
while (true) {
semaphore.acquire(); // 获取信号量
Thread.sleep(100); // 模拟购票操作
if (remindTickets <= 0) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "已售空...");
semaphore.release(); // 释放信号量
break; // 票已售空,窗口停止售票(终止while)
} else {
remindTickets--; // 票数-1
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "售出1张票,现余票为" + remindTickets);
}
semaphore.release(); // 释放信号量
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建4个窗口
for (int i = 1; i <= 4; i++) {
new Thread(new TicketWindow(), "窗口" + i).start();
}
}
}
④ ReentrantLock 锁
// 思路4:ReentrantLock 可重入锁
public class Solution010_06 {
static int remindTickets = 20; // 余票定义
static ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
// 窗口定义
static class TicketWindow implements Runnable {
@SneakyThrows
@Override
public void run() {
// 模拟售票操作
while (true) {
lock.lock(); // 加锁
Thread.sleep(100); // 模拟购票操作
if (remindTickets <= 0) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "已售空...");
break; // 票已售空,窗口停止售票(终止while)
} else {
remindTickets--; // 票数-1
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "售出1张票,现余票为" + remindTickets);
}
lock.unlock(); // 释放锁
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建4个窗口
for (int i = 1; i <= 4; i++) {
new Thread(new TicketWindow(), "窗口" + i).start();
}
}
}
11.有一批任务Tasks,现在需要实现按批次执行,并且批次可以动态指定,例如[1,3,5,7]第一批执行,[11,13,15,17]第二批执行,…,最后没有指定的任务就最后一起执行掉。批次之间需要按顺序,前一批执行完了才执行下一批
核心:通过Future的批次执行和等待结果确认来实现任务的批次等待
/**
* 按照指定批次执行任务,可指定任务索引进行批量执行
* 1.定义任务MyTask
* 2.构建一个创建批量任务的方法
* 3.构建一个批量执行任务的方法(入参:要执行的任务列表,要执行的任务批次,根据批次依次进行执行)
* - 根据批次依次执行,记录已执行的任务索引
* - 等待批次任务执行完成(通过Future提供的get方法进行确认),最后执行剩余的任务
*/
public class Solution1 {
// 批量创建任务
public List<MyTask> createTaskList(int num) {
List<MyTask> list = new ArrayList<MyTask>();
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
MyTask task = new MyTask(i);
list.add(task);
}
return list;
}
// 批量执行任务
public void executeTask(List<MyTask> list,List<List<Integer>> batchList) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
// 创建固定大小的线程池
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
// 定义已执行的索引序列
List<Integer> hasExecuteIndex = new ArrayList<>();
// 根据指定的批次信息执行任务
for (int i = 0; i < batchList.size(); i++) {
// 将要执行的批次准备好,批量执行指定索引的任务
List<Future<Void>> futures = new ArrayList<>();
for(int idx : batchList.get(i)) {
Future<Void> future = (Future<Void>) executor.submit(list.get(idx));
futures.add(future);
hasExecuteIndex.add(idx);
}
// 等待一批任务完成
for (Future<Void> future : futures) {
future.get(); // 等待每个任务执行完成
}
// 清理futures,进入下一批次的执行
futures.clear();
System.out.println("当前批次" + i + "执行完成");
}
// 执行剩下任务
List<Future<Void>> lastFuture = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
// 执行未执行的任务
if(!hasExecuteIndex.contains(i)) {
lastFuture.add((Future<Void>) executor.submit(list.get(i)));
}
}
// 关闭线程池并等待所有任务完成
executor.shutdown();
while(!executor.isTerminated()) {
// 纯等待
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
Solution1 s = new Solution1();
// 批量创建任务
List<MyTask> list = s.createTaskList(100);
// 定义执行批次
List<List<Integer>> batchList = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> batch1 = Arrays.asList(1,3,5,7);
List<Integer> batch2 = Arrays.asList(11,13,15,17);
batchList.add(batch1);
batchList.add(batch2);
// 调用方法执行批次
s.executeTask(list,batchList);
}
}
class MyTask implements Runnable{
private int taskId;
public MyTask(int taskId) {
this.taskId = taskId;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"线程执行" + taskId + "任务");
}
}
12.JAVA 实现单例模式
① 饿汉式
/**
* 12.java 实现单例模式
* - 饿汉式(在定义的时候就构建对象)
*/
public class Singleton02 {
// 1.构建一个静态的私有的自身的对象
private static Singleton02 singleton = new Singleton02();
// 2.构造函数私有化
public Singleton02() {
}
// 3.对外提供一个获取该单例对象的入口
public static Singleton02 getSingleton(){
return singleton;
}
}
② 懒汉式
懒汉式(线程不安全)
/**
* 12.java 实现单例模式
* - 懒汉式(只有在使用到的时候才创建对象)
*/
public class Singleton01 {
// 1.构建一个静态的私有的自身的对象
private static Singleton01 singleton;
// 2.构造函数私有化
public Singleton01() {
}
// 3.对外提供一个获取该单例对象的入口
public static Singleton01 getSingleton(){
if(singleton==null){
singleton = new Singleton01();
}
return singleton;
}
}
懒汉式(线程安全):锁、双检锁
/**
* 12.java 实现单例模式
* - 懒汉式(只有在使用到的时候才创建对象)
* - 多线程思路改造(考虑线程安全问题)
*/
public class Singleton03 {
// 1.构建一个静态的私有的自身的对象
private static volatile Singleton03 singleton; // volatile 避免指令重排序问题
// 2.构造函数私有化
public Singleton03() {
}
// 3.对外提供一个获取该单例对象的入口
/*
public static Singleton03 getSingleton1(){
synchronized (Singleton03.class){
if(singleton==null){
singleton = new Singleton03();
}
}
return singleton;
}
*/
public static synchronized Singleton03 getSingleton2() {
if (singleton == null) {
singleton = new Singleton03();
}
return singleton;
}
// 双检锁模式
public static Singleton03 getSingleton() {
if (singleton == null) {
synchronized (Singleton03.class) {
if (singleton == null) {
singleton = new Singleton03();
}
}
}
return singleton;
}
}
③ 枚举
/**
* 12.java 实现单例模式
* - 枚举
*/
public class Singleton04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Single single = Single.SINGLE;
single.print();
}
// 构建枚举
enum Single{
SINGLE;
private Single(){
}
public void print(){
System.out.println("hello world");
}
}
}
13.手撕:生产者-消费者模式
理解生产者-消费者模式的核心,简单来说就是生产者不断生产数据,消费者不断消费数据,这种设计模式需要满足三个条件要求:
- ① 生产、消费:生产者生产数据到缓冲区中,消费者从缓冲区中取数据
- ② 缓冲区满:如果缓冲区已满,则生产者线程阻塞(即可以理解为盘子装不下,不能继续生产太多,因此暂停生产)
- ③ 缓冲区空:如果缓冲区为空,则消费者线程阻塞(即可以理解为盘子空了,没有数据可用,就算消费者过来也是空转一趟)
代码设计分析:
- ① 缓冲队列设计:选择一个集合充当缓存,设定缓存限制(盘子容量),缓冲队列只有两种操作行为(生产数据、消费数据)
- ② 线程设计:生产者线程、消费者线程
- 生产者线程:调用缓存队列的生产行为
- 消费者线程:调用缓存队列的消费行为
生产者-消费者的实现方式:
- ①
synchronized+wait+notify方式 - ② 可重入锁
ReentrantLock+ 多Condition - ③
BlockingQueue阻塞队列方式
① synchronized + wait + notify 方式
缓冲区与计数:使用数组
buffer[]作为缓冲区,通过count跟踪当前缓冲区的元素数量- 缓冲区设计:
- (1)可以选用循环数组
buffer[]来实现,需要自行维护【下一个读取/写入】的位置(自行维护指针)、缓冲区大小、缓冲元素总个数等要素 - (2)也可以基于现有的队列
Queue<Object>来实现
- (1)可以选用循环数组
- 缓冲区设计:
生产者设计:
- (1)生产者在无限循环中尝试生产数据
- (2)当缓冲区满的时候,调用
wait方法阻塞生产者线程 - (3)如果缓冲区未满(有空位),则生产数据并更新当前缓冲区状态,生产完成调用
notify方法唤醒可能在等待的消费者线程
消费者设计:
- (1)消费者在无限循环中尝试消费数据
- (2)当缓冲区空的时候,调用
wait方法阻塞消费者线程 - (3)如果缓冲区不为空(有数据可消费),则消费数据并更新当前缓冲区状态,消费完成调用
notify方法唤醒可能在等待的生产者线程
/**
* 生产者、消费者模式 - 基于 synchronized 实现
*/
public class ProducerConsumerWithSync {
// 定义缓冲区和计数器
static int BUFFER_SIZE = 10; // 限定缓冲区大小为10
static int count = 0; // 当前缓冲区元素个数
static Object[] buffer = new Object[BUFFER_SIZE]; // 定义缓冲区
// 定义索引位置
static int in = 0; // 下一个将元素放入缓冲区的索引位置
static int out = 0;// 下一个要从缓冲区中取出元素的索引位置
// 定义锁(对象锁)
static Object lock = new Object();
// 定义生产者类(生产者线程)
static class Producer extends Thread {
@SneakyThrows
@Override
public void run() {
// 生产者不断尝试生产数据
while (true) {
synchronized (lock) {
// 如果缓冲区满则阻塞生产
while (count == BUFFER_SIZE) { // 当前缓冲区数据个数达到缓冲区大小(此处不用in判断)
System.out.println("当前缓冲区已满,停止生产...");
lock.wait();
}
// 如果缓冲区有空位,则生产数据并唤醒在等待的消费者线程
int num = new Random().nextInt(10000);
buffer[in] = num; // 生产一个随机数据
in = (in + 1) % BUFFER_SIZE; // in 指针指向下一个位置
count++; // 元素个数+1
System.out.println("生产者生产了一个数据" + num);
// 唤醒消费者线程
lock.notify();
// 模拟生产数据耗时
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}
}
}
// 定义消费者类(消费者线程)
static class Consumer extends Thread {
@SneakyThrows
@Override
public void run() {
// 消费者不断尝试消费数据
while (true) {
synchronized (lock) {
// 如果缓冲区空则阻塞消费
while (count == 0) {
System.out.println("当前缓冲区已空,停止消费....");
lock.wait();
}
// 如果缓冲区有数据可用,则消费数据并唤醒在等待的生产者线程
int num = (int) buffer[out]; // 取出数据
out = (out + 1) % BUFFER_SIZE; // out 指针指向下一个位置
count--; // 元素个数-1
System.out.println("消费者消费了一个数据" + num);
// 唤醒生产线程
lock.notify();
// 模拟消费数据耗时
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 测试
Producer producer = new Producer();
Consumer consumer = new Consumer();
producer.start(); // 启动生产者线程
consumer.start(); // 启动消费者线程
}
}
测试说明:部分情况下测试数据展示的结果看起来好像是先生产一批、然后消费一批、再生产、再消费,有种生产完成了之后再切换线程消费的感觉。可以试着调整生产和消费的速率,多观察几组数据,生产者和消费者是各自执行的,当缓冲区达到一定条件的时候会触发线程的阻塞状态(例如缓冲区满则阻塞生产线程、缓冲区空则阻塞消费线程)。
生产者生产了一个数据8768
消费者消费了一个数据8768
当前缓冲区已空,停止消费....
生产者生产了一个数据1592
生产者生产了一个数据2072
生产者生产了一个数据9673
消费者消费了一个数据1592
消费者消费了一个数据2072
消费者消费了一个数据9673
生产者生产了一个数据6021
生产者生产了一个数据8217
生产者生产了一个数据215
生产者生产了一个数据9222
生产者生产了一个数据5691
生产者生产了一个数据1786
消费者消费了一个数据6021
生产者生产了一个数据3274
消费者消费了一个数据8217
另一种写法版本(借助Queue简化设计,核心思路不变)
- 代码核心设计思路
- ① 定义缓冲区(
Queue)、设置缓冲区大小 - ② 定义生产方法(生产数据)、消费方法(消费数据)
- ③ 开启生产者线程(调用生产方法)、开启消费者线程(调用消费方法)
- ① 定义缓冲区(
/**
* 生产者、消费者模式 - 基于 synchronized 实现
*/
public class ProducerConsumerWithSyncAndQueue {
static int BUFFER_SIZE = 10; // 设置缓冲区大小(上限)
static Queue<Integer> buffer = new LinkedList<>(); // 定义缓冲区
static Object lock = new Object(); // 定义锁(对象锁)
// 定义生产方法
public void produce() {
// 定义生产者线程
Thread producer = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@SneakyThrows
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
synchronized (lock) {
while (buffer.size() == BUFFER_SIZE) {
System.out.println("当前缓冲区满,停止生产......");
// 缓冲区满,阻塞生产者线程
lock.wait();
}
// 缓冲区未满,随机生产数据
int num = new Random().nextInt(100);
buffer.add(num);
System.out.println("生产者生产一个数据:" + num);
// 唤醒可能在等待的消费者线程
lock.notify();
// 模拟生产时耗
Thread.sleep(10);
}
}
}
});
// 启动生产者线程
producer.start();
}
// 定义消费方法
public void consume() {
// 定义消费者线程
Thread consumer = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@SneakyThrows
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
synchronized (lock) {
// 当缓冲区为空,停止消费
while (buffer.size() == 0) {
lock.wait();
}
// 缓冲区不为空则继续消费数据
int getNum = buffer.poll();
System.out.println("消费者取出一个数据:" + getNum);
// 唤起其他可能在等待的生产者
lock.notify();
}
// 模拟消费耗时
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}
});
// 启动消费者线程
consumer.start();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 测试
ProducerConsumerWithSyncAndQueue test = new ProducerConsumerWithSyncAndQueue();
test.produce(); // 调用生产者方法
test.consume(); // 调用消费者方法
}
}
/**
* 生产者、消费者模式 - 基于 synchronized 实现
*/
public class ProducerConsumerWithSyncAndQueue2 {
static int BUFFER_SIZE = 10; // 设置缓冲区大小(上限)
static Queue<Integer> buffer = new LinkedList<>(); // 定义缓冲区
static Object lock = new Object(); // 定义锁(对象锁)
@SneakyThrows
// 定义生产方法
public void produce() {
while (true) {
synchronized (lock) {
while (buffer.size() == BUFFER_SIZE) {
System.out.println("当前缓冲区满,停止生产......");
// 缓冲区满,阻塞生产者线程
lock.wait();
}
// 缓冲区未满,随机生产数据
int num = new Random().nextInt(100);
buffer.add(num);
System.out.println("生产者生产一个数据:" + num);
// 唤醒可能在等待的消费者线程
lock.notify();
// 模拟生产时耗
Thread.sleep(10);
}
}
}
@SneakyThrows
// 定义消费方法
public void consume() {
while (true) {
synchronized (lock) {
// 当缓冲区为空,停止消费
while (buffer.size() == 0) {
lock.wait();
}
// 缓冲区不为空则继续消费数据
int getNum = buffer.poll();
System.out.println("消费者取出一个数据:" + getNum);
// 唤起其他可能在等待的生产者
lock.notify();
}
// 模拟消费耗时
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 测试
ProducerConsumerWithSyncAndQueu2 test = new ProducerConsumerWithSyncAndQueu2();
// 定义生产者线程
Thread producer = new Thread(() -> {
test.produce(); // 调用生产者方法
});
// 定义消费者线程
Thread consumer = new Thread(() -> {
test.consume(); // 调用消费者方法
});
// 启动线程
producer.start();
consumer.start();
}
}
② 可重入锁ReentrantLock + 多Condition
ReentrantLock 是 Java 中 java.util.concurrent.locks 包下的一个类,实现了 Lock 接口。它提供了与 synchronized 关键字类似的功能,但更加灵活和强大
Condition 是 ReentrantLock 提供的一个条件变量,用于实现线程间的等待/通知机制
一个 ReentrantLock 可以关联多个 Condition,每个 Condition 可以用于不同的等待条件,通过使用ReentrantLock + 多 Condition 的组合,可以精确控制哪些线程被唤醒,而不是像是notify那样随机唤醒一个线程
// 初始化
ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
Condition condition = lock.newCondition();
// 线程1
lock.lock();
try {
while (/* 条件不满足 */) {
condition.await(); // 当前线程等待
}
// 条件满足,执行操作
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
// 线程2
lock.lock();
try {
// 改变条件
condition.signal(); // 唤醒一个等待的线程
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
通过结合 ReentrantLock 和多个 Condition,可以实现更复杂的线程同步机制。例如,在一个生产者-消费者模型中,可以使用两个 Condition 分别控制生产者和消费者的等待与唤醒。通过这种方式,开发者可以更灵活地控制多线程程序的执行顺序和资源访问,避免竞争条件和死锁等问题
notFull条件用于控制生产者线程,当缓冲区满时,生产者线程等待await()方法notEmpty条件用于控制消费者线程,当缓冲区空时,消费者线程等待await()方法- 通过
signal()方法,生产者可以唤醒消费者,消费者可以唤醒生产者,从而实现线程间的协作
/**
* 生产者、消费者模式
*/
public class ProducerConsumerWithLock {
// 定义缓冲区和计数器
static int BUFFER_SIZE = 10; // 限定缓冲区大小为10
static int count = 0; // 当前缓冲区元素个数
static Object[] buffer = new Object[BUFFER_SIZE]; // 定义缓冲区
// 定义索引位置
static int in = 0; // 下一个将元素放入缓冲区的索引位置
static int out = 0;// 下一个要从缓冲区中取出元素的索引位置
// 定义锁
static ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
// 多Condition
static Condition notFull = lock.newCondition(); // 缓冲区未满(表示生产者可以进行生产的条件)
static Condition notEmpty = lock.newCondition(); // 缓冲区不为空(表示消费者可以进行消费的条件)
// 定义生产者类(生产者线程)
static class Producer extends Thread {
@SneakyThrows
@Override
public void run() {
// 生产者不断尝试生产数据
while (true) {
lock.lock();
// 如果缓冲区满则阻塞生产
while (count == BUFFER_SIZE) { // 当前缓冲区数据个数达到缓冲区大小(此处不用in判断)
System.out.println("当前缓冲区已满,停止生产...");
notFull.await();
}
// 如果缓冲区有空位,则生产数据并唤醒在等待的消费者线程
int num = new Random().nextInt(10000);
buffer[in] = num; // 生产一个随机数据
in = (in + 1) % BUFFER_SIZE; // in 指针指向下一个位置
count++; // 元素个数+1
System.out.println("生产者生产了一个数据" + num);
// 唤醒生产者线程
notEmpty.signal();
// 模拟生产数据耗时
Thread.sleep(1000);
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
// 定义消费者类(消费者线程)
static class Consumer extends Thread {
@SneakyThrows
@Override
public void run() {
// 消费者不断尝试消费数据
while (true) {
lock.lock();
// 如果缓冲区空则阻塞消费
while (count == 0) {
System.out.println("当前缓冲区已空,停止消费....");
notEmpty.await();
}
// 如果缓冲区有数据可用,则消费数据并唤醒在等待的生产者线程
int num = (int) buffer[out]; // 取出数据
out = (out + 1) % BUFFER_SIZE; // out 指针指向下一个位置
count--; // 元素个数-1
System.out.println("消费者消费了一个数据" + num);
// 唤醒消费者线程
notFull.signal();
// 模拟消费数据耗时
Thread.sleep(1000);
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 测试
Producer producer = new Producer();
Consumer consumer = new Consumer();
producer.start(); // 启动生产者线程
consumer.start(); // 启动消费者线程
}
}
基于Queue简化版本
/**
* 生产者、消费者模式
*/
public class ProducerConsumerWithLockAndQueue {
static int BUFFER_SIZE = 10; // 限定缓冲区大小为10
static Queue<Integer> buffer = new LinkedList<>(); // 定义缓冲区
// 定义锁
static ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
// 多Condition
static Condition notFull = lock.newCondition(); // 缓冲区未满(表示生产者可以进行生产的条件)
static Condition notEmpty = lock.newCondition(); // 缓冲区不为空(表示消费者可以进行消费的条件)
@SneakyThrows
// 定义生产方法
public void produce() {
while (true) {
lock.lock();
while (buffer.size() == BUFFER_SIZE) {
System.out.println("当前缓冲区已满,停止生产...");
notFull.await();
}
int num = new Random().nextInt(1000);
System.out.println("生产者生产数据:" + num);
buffer.add(num);
// 唤醒可能正在等待的消费者线程
notEmpty.signal();
// 模拟生产耗时
Thread.sleep(1000);
lock.unlock();
}
}
@SneakyThrows
// 定义消费方法
public void consume() {
while (true) {
lock.lock();
while (buffer.size() == 0) {
System.out.println("当前缓冲区已空,停止消费...");
notEmpty.await();
}
int num = buffer.poll();
System.out.println("消费者消费数据:" + num);
// 唤醒可能正在等待的生产者线程
notFull.signal();
// 模拟消费耗时
Thread.sleep(100);
lock.unlock();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 测试
ProducerConsumerWithLockAndQueue test = new ProducerConsumerWithLockAndQueue();
// 创建生产者线程
Thread producer = new Thread(() -> {
test.produce();
});
// 创建消费消费者线程
Thread consumer = new Thread(() -> {
test.consume();
});
// 启动线程
producer.start();
consumer.start();
}
}
③ BlockingQueue 阻塞队列方式
BlockingQueue 是 Java 并发包 (java.util.concurrent) 中提供的一个线程安全的队列实现,它支持阻塞操作。当队列为空时,消费者线程会被阻塞,直到队列中有数据;当队列满时,生产者线程会被阻塞,直到队列有空闲空间。这种方式非常适合实现生产者-消费者模式
BlockingQueue的核心方法put(E e):将元素放入队列,如果队列已满,则阻塞直到队列有空闲空间take():从队列中取出元素,如果队列为空,则阻塞直到队列中有元素offer(E e):将元素放入队列,如果队列已满,则返回false,不会阻塞poll():从队列中取出元素,如果队列为空,则返回null,不会阻塞
生产者-消费者模式实现代码核心
- ① 创建
BlockingQueue阻塞队列(初始化容量)- 如果队列满,则阻塞生产者线程;如果队列空,则阻塞消费者线程
- ② 生产方法(生产者线程)
- 调用
put方法将数据放入队列,如果队列已满则会阻塞直到队列有空闲空间
- 调用
- ③ 消费方法(消费者线程)
- 调用
take方法从队列中取出数据,如果队列为空则会阻塞直到队列中有数据
- 调用
- ① 创建
适用场景分析
- 适用场景:生产者-消费者模式、任务调度系统、线程池任务队列
- 生产者-消费者模式分析:通过
BlockingQueue,可以轻松实现生产者-消费者模式,避免手动管理线程同步的复杂性
/**
* 基于BlockingQueue实现生产者、消费者模式
*/
public class ProducerConsumerWithBlockingQueue {
// 创建一个容量为 10 的阻塞队列
BlockingQueue<Integer> queue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(10);
@SneakyThrows
// 生产方法
public void produce() {
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
queue.put(i); // 生产数据
System.out.println("生产者生产: " + i);
Thread.sleep(1000); // 模拟生产耗时
}
}
@SneakyThrows
// 消费方法
public void consume() {
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
int value = queue.take(); // 消费数据
System.out.println("消费者消费: " + value);
Thread.sleep(2000); // 模拟消费耗时
}
}
@SneakyThrows
public static void main(String[] args) {
ProducerConsumerWithBlockingQueue test = new ProducerConsumerWithBlockingQueue();
// 创建生产者线程
Thread producer = new Thread(() -> {
test.produce();
});
// 创建消费者线程
Thread consumer = new Thread(() -> {
test.consume();
});
// 启动生产者和消费者线程
producer.start();
consumer.start();
// 等待线程结束
producer.join();
consumer.join();
System.out.println("生产者和消费者任务完成!");
}
}