泛型
...大约 4 分钟
泛型
泛型引入
需求分析
编写程序,在ArrayList中,添加3个Dog对象。Dog对象含有name和age,并输出name和age (要求使用getXxx())
定义一个ArrayList,将小狗的信息装入,如果这个时候不小心混入一只小猫,则在处理过程中可能需要手动转化
先使用传统的方法来解决->引出泛型
public class DogDemo{
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 传统方式引入
ArrayList dogs = new ArrayList();
dogs.add(new Dog("小黄",1));
dogs.add(new Dog("大白",2));
dogs.add(new Dog("小牛",3));
// 混入一只cat
dogs.add(new Cat("花小猫",1,"我是一只猫"));
// 方式1:遍历数据(由于实体重写了toString,此处打印出来的是对象的toString,不需要额外转化)
for (int i = 0; i < dogs.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(dogs.get(i));
}
System.out.println("---------------- 分割线 ----------------");
// 方式2:假设默认dogs里面都是Dog类型,并不知道混进去一只Cat
for(Object dog : dogs){
// 向下转型:Object=》Dog
Dog d = (Dog) dog;
System.out.println(d);
}
}
}
class Dog {
public String name;
public int age;
public Dog(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Dog{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
// 猫定义
class Cat {
public String name;
public int age;
public String descr;
public Cat(String name, int age, String descr) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.descr = descr;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Cat{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", descr='" + descr + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
基于上述的内容分析,如果没有指定列表存储的数据类型,则可以加入任何Object,当数据列表中出现了预期之外的数据格式对象,则在遍历处理的时候就会出现问题(需要额外单独处理)
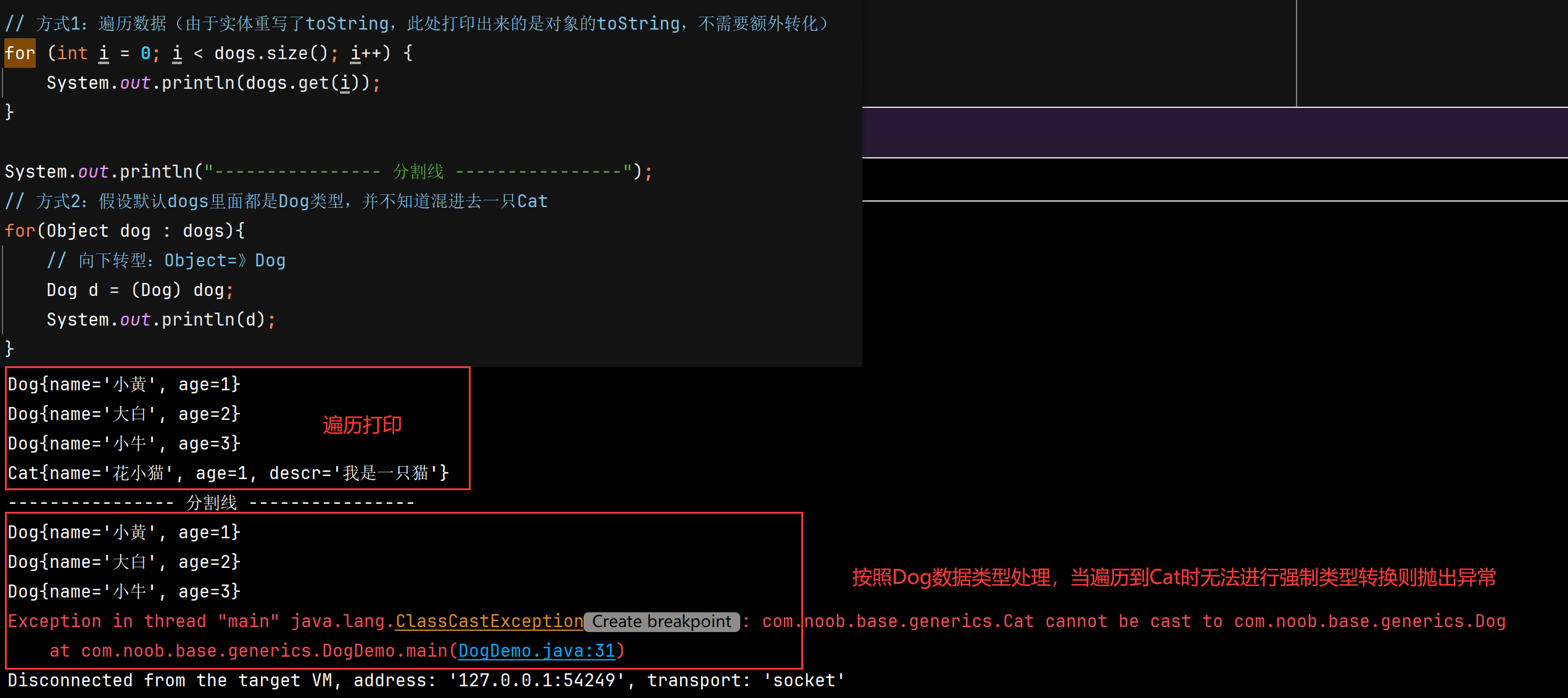
因此基于这种方式衍生两个问题:
- 安全性:无法对加入到集合ArrayList的数据类型进行约束
- 遍历的时候需要进行类型转换,如果集合数据量比较大则对效率有影响
因此引入泛型进行约束,进而解决上面的问题
// 引用泛型
ArrayList<Dog> dogs = new ArrayList<>();
dogs.add(new Dog("小黄", 1));
dogs.add(new Dog("大白", 2));
dogs.add(new Dog("小牛", 3));
// 混入一只cat 此时无法混入,因为dogs约束了添加元素必须为Dog对象
// dogs.add(new Cat("花小猫", 1, "我是一只猫"));
引入泛型具备的好处:
- 编译时检查添加元素的类型,提高安全性
- 减少类型转换的次数,提高效率(其分析如下)
- 不引入泛型:Dog =》转化为Object加入列表=》取出时需要将Object转化为Dog
- 引入泛型:数据存入和取出都是Dog(不需额外的数据类型转化处理)
泛型的作用:可以在类声明时通过一个标识表示类中某个属性的类型,或者是某个方法的返回类型、或者是参数类型
泛型语法
泛型声明
interface 接口<T>{}
class 类<K,V>{}
// 其中T、K、V不代表值,而是表示类型,可以使任意字母(一般用T,是Type缩写)
泛型实例化
List<String> strList = new ArrayList<String>();
Iterator<Customer> iterator = customers.iterator();
注意事项:
1. interface List<T>{} ,public class HashSet<E> {}..等等
说明: T, E只能是引用类型
List< Integer> list = new ArrayList< Integer> (); //OK
List<int> list2 = new ArrayList <int> 0)://错误
2. 在给泛型指定具体类型后,可以传入该类型或者其子类类型
3. 泛型使用形式
List<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList <Integer> ();
List< Integer> list2 = new ArrayList<> (); [说明:]
3. List list3 = new ArrayList(); # 默认给它的泛型是[<E> E就是Object
泛型案例
定义Employee类
1)该类包含: private成员变量name,sal,birthday, 其中birthday为MyDate类的对象;
2)为每一个属性定义getter, setter方法;
3)重写toString方法输出name, sal, birthday
4)MyDate类包含: private成员变量month,day,year; 并为每一个属性定义getter,setter方法;
5)创建该类的3个对象,并把这些对象放入ArrayList集合中(ArrayList需使用泛型来定义),对集合中的元素进行排序,并遍历输出:
排序方式:调用ArrayList 的sort方法,传入Comparator对象[使用泛型],先按照name排序,如果name相同,则按生日日期的先后排序。( 即:定制排序)
public class Employee {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Employee> employeeList = new ArrayList<Employee>();
Employee e1 = new Employee("小C",1000,new MyDate(2004,03,23));
Employee e2 = new Employee("小C",10000,new MyDate(1997,05,24));
Employee e3 = new Employee("小A",8000,new MyDate(1968,12,16));
employeeList.add(e1);
employeeList.add(e2);
employeeList.add(e3);
Comparator comparator = new Comparator<Employee>() {
@Override
public int compare(Employee o1, Employee o2) {
// 姓名相同比较年份
if(o1.getName().equals(o2.getName())){
return o1.getBirthDay().toString().compareTo(o2.getBirthDay().toString());
}else {
return o1.getName().compareTo(o2.getName());
}
}
};
employeeList.sort(comparator);
for(Employee employee : employeeList){
System.out.println(employee);
}
}
private String name;
private double sal;
private MyDate birthDay;
public Employee(String name, double sal, MyDate birthDay) {
this.name = name;
this.sal = sal;
this.birthDay = birthDay;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getSal() {
return sal;
}
public void setSal(double sal) {
this.sal = sal;
}
public MyDate getBirthDay() {
return birthDay;
}
public void setBirthDay(MyDate birthDay) {
this.birthDay = birthDay;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Employee{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", sal=" + sal +
", birthDay=" + birthDay +
'}';
}
}
class MyDate{
private int year;
private int month;
private int day;
public MyDate(int year, int month, int day) {
this.year = year;
this.month = month;
this.day = day;
}
public int getYear() {
return year;
}
public void setYear(int year) {
this.year = year;
}
public int getMonth() {
return month;
}
public void setMonth(int month) {
this.month = month;
}
public int getDay() {
return day;
}
public void setDay(int day) {
this.day = day;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return year + "-" + month + "-" + day;
}
}
Powered by Waline v3.1.3